Next: The Lego Ball Sorter, Previous: A Simple State Machine, Up: Getting Started [Contents][Index]
4.3 A Camera Example
The Camera example introduces the system component
(See Systems). The system diagram (See Invoking dzn graph) looks
like this:
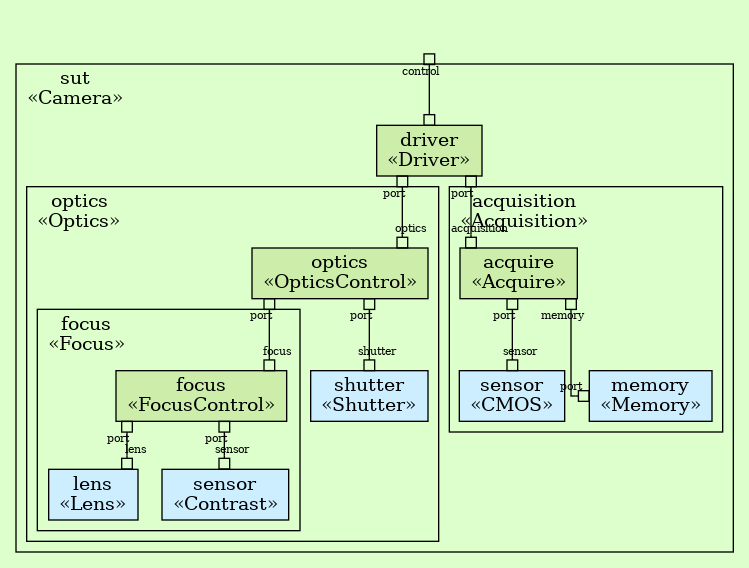
This is what the Camera system looks like in Dezyne:
component Camera
{
provides IControl control;
system
{
Driver driver;
Acquisition acquisition;
Optics optics;
control <=> driver.control;
driver.acquisition <=> acquisition.port;
driver.optics <=> optics.port;
}
}
It introduces the following concepts:
provides IControl control;Similar to a regular component, it defines ports,
systemThe
systemspecification defines instances of components and their bindings,Driver driver;A component instance named
driverof typeDriver,Acquisition acquisition;A component instance named
acquisitionof typeAcquisition, which is asystemcomponent itself,Optics optics;An instance of another
systemcomponent,control <=> driver.control;A binding of the
Camera’s portcontrolto the port namedcontrolof thedriverinstance.driver.acquisition <=> acquisition.port;A binding between pairs of ports on component instances.
The light blue components in the system view, such as lens are
foreign components (See Components); their definition
looks like this:
component Lens
{
provides ILens port;
}
A foreign component does not specify any implementation: neither a
behavior nor a system; its behavior is said to be
implementation elsewhere, and in a foreign language (in this case
C++).
The full example is contained in the source tree at test/all/Camera/Camera.dzn or Camera.dzn.
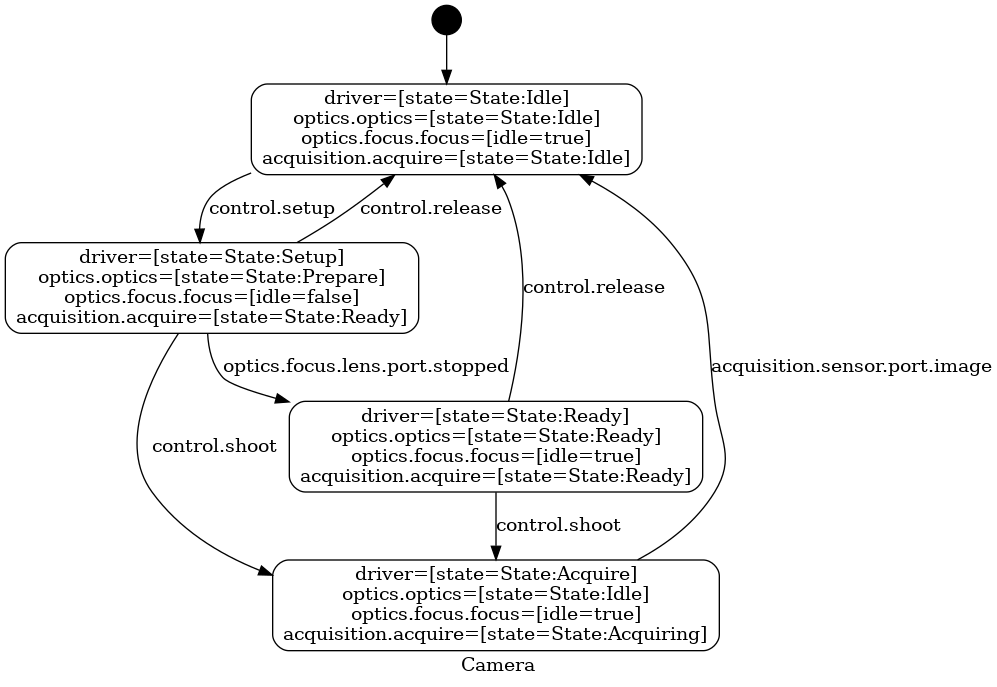
The simplified5 state diagram: